Our network of roads comprise of major roads and minor roads, but what exactly are major and minor roads and how can you tell the difference?
If you know the name of the road that you’re driving on, then this is the first clue as to the type of road you’re traveling on. It will help to establish if you are driving on a major or minor road, or a primary or non-primary route.
Major Roads
Major roads are defined as either the ‘Major Road Network’ (motorways), or the Primary Route Network (primary ‘A’ roads).
Motorways (M Roads)
‘M’ roads are high speed major routes with a maximum speed of 70 mph (110 km/h) and listed in the colour blue on road maps. If the road you are driving on begins with the letter ‘M’, for example the M1, then you’re on a motorway. A motorway may also end with the letter ‘M’, for example the A1(M).

Another indication that you’re driving on a motorway (major road) is the use of blue signs that are only used on motorways (see Major, primary route motorway sign). Motorways are defined by the Department for Transport as the ‘Major Road Network’, or the network of motorways.

PRIMARY ROUTES (A ROADS)
Primary ‘A’ roads are major routes that often connect towns and cities and are coloured green on most road maps and make up the Primary Route Network. The Primary Route Network is a designation of roads that are linking places of importance from a traffic perspective, and one that links all these destinations throughout the UK by easily identifiable routes.
Primary ‘A’ roads are often dual carriageways (see primary route dual carriageway sign), which make use of green road signs with white text and have a maximum speed limit of 70 mph. Primary routes will have the prefix letter ‘A’ followed by a number; for example the A1.
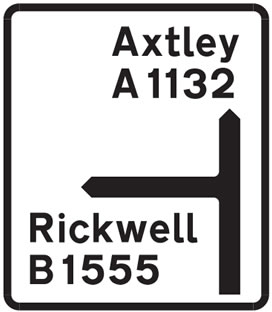
NON-PRIMARY ROUTES (A ROADS)
Non-primary routes that are still ‘A’ roads are often single carriageway and make use of white signs with black text (see Major road, Non-primary route ‘A’ road sign) and have a maximum speed limit of 60 mph.
Minor Roads
Definition of a minor road is:

NON-PRIMARY ROUTES (B ROADS)
‘B’ roads are often narrower than ‘A’ roads, are usually less busy and are used to interconnect towns and villages. Speed limits vary from 20 mph often in residential areas, and in rural locations up to a maximum of 60 mph. Non-primary routes will have the prefix letter ‘B’ followed by a number; for example the B1264. On rare occasions, a ‘B’ road is categorised as a primary route.
Major and Minor Roads
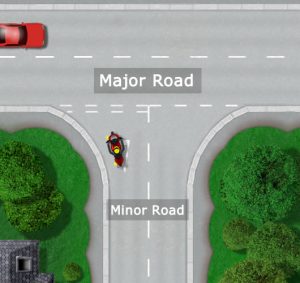
A minor road is typically defined as a road of less importance to the one it is joining. It could be referred to as a ‘B’ road or a ‘side’ road. The occasional minor road may in fact be so minor that it remains uncategorised and may not appear on certain road maps.
Not to be confused with motorways and the ‘Major Road Network’, major and minor roads are typically used by motorists to define roads on their level of significance. As can be seen in the diagram ‘Major and Minor roads’, the term ‘major road’ is defined as the larger main road, where smaller minor roads join via junctions from either side.
TUTORIALS RELATED TO JUNCTIONS
- Road junctions
- Turning left at a junction
- Turning right at a junction
- Box junction
- Staggered junction
- Y Junctions
- Junction lines
- Junction signs
- Emerging from a junction
- Creep and peep
